
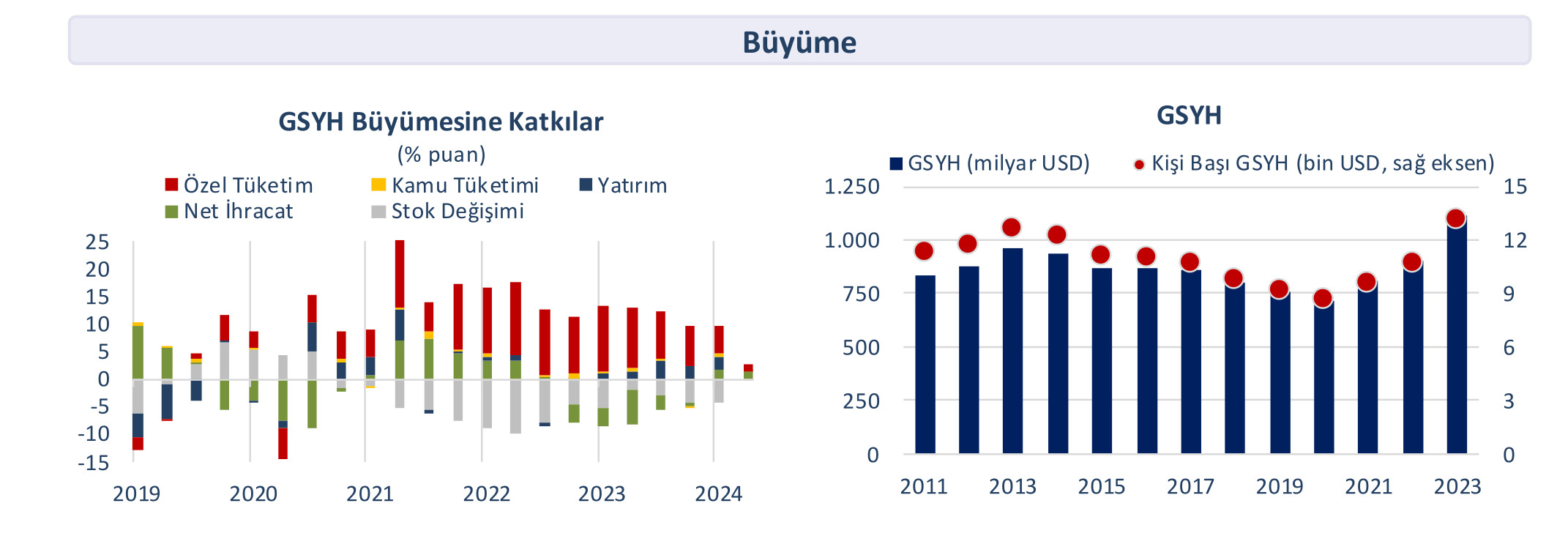
Turkey's economy continued its recovery process in the first nine months of 2024. Our economy grew by 5.7 percent in the first quarter of 2024 and by 2.5 percent in the second quarter. According to IMF estimates, the economy is expected to grow by 3.1 percent in 2024 and 3.2 percent in 2025, respectively. Industrial production contracted by 3.9 percent year-on-year in September. Unemployment decreased to 8.8 percent. Inflation expectations continued their downward trend compared to the previous month in September, realizing at 2.54 percent.
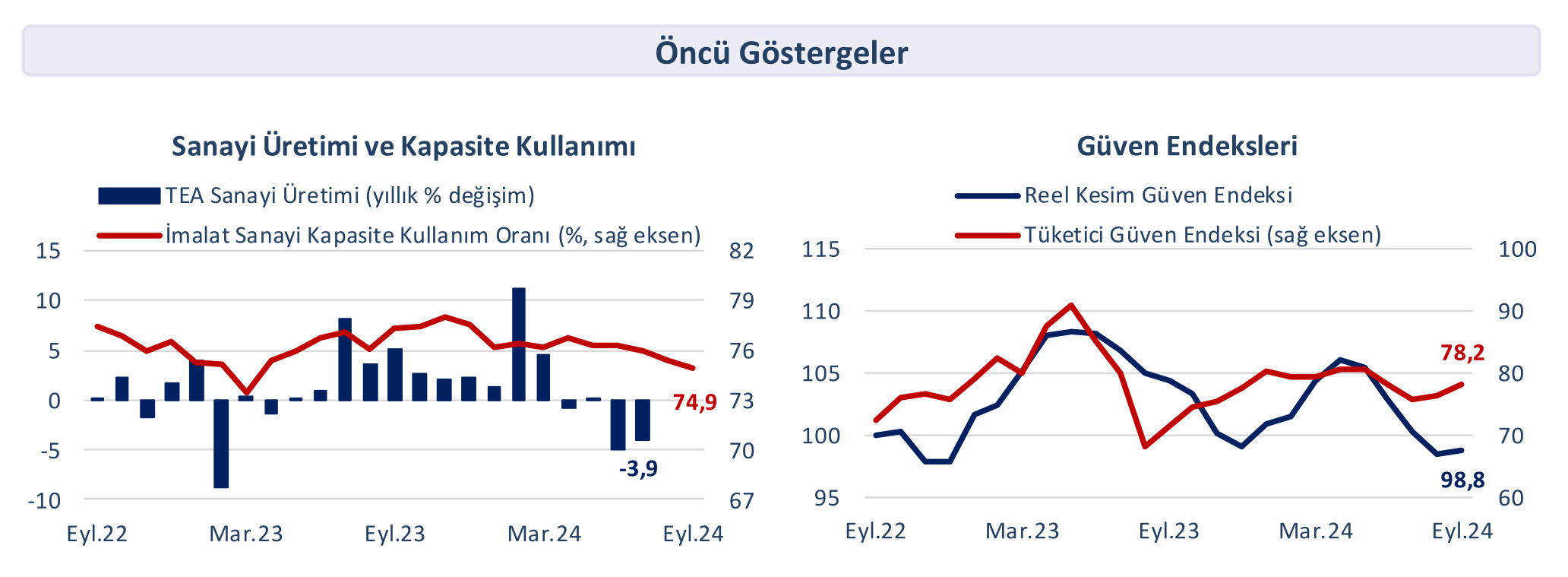
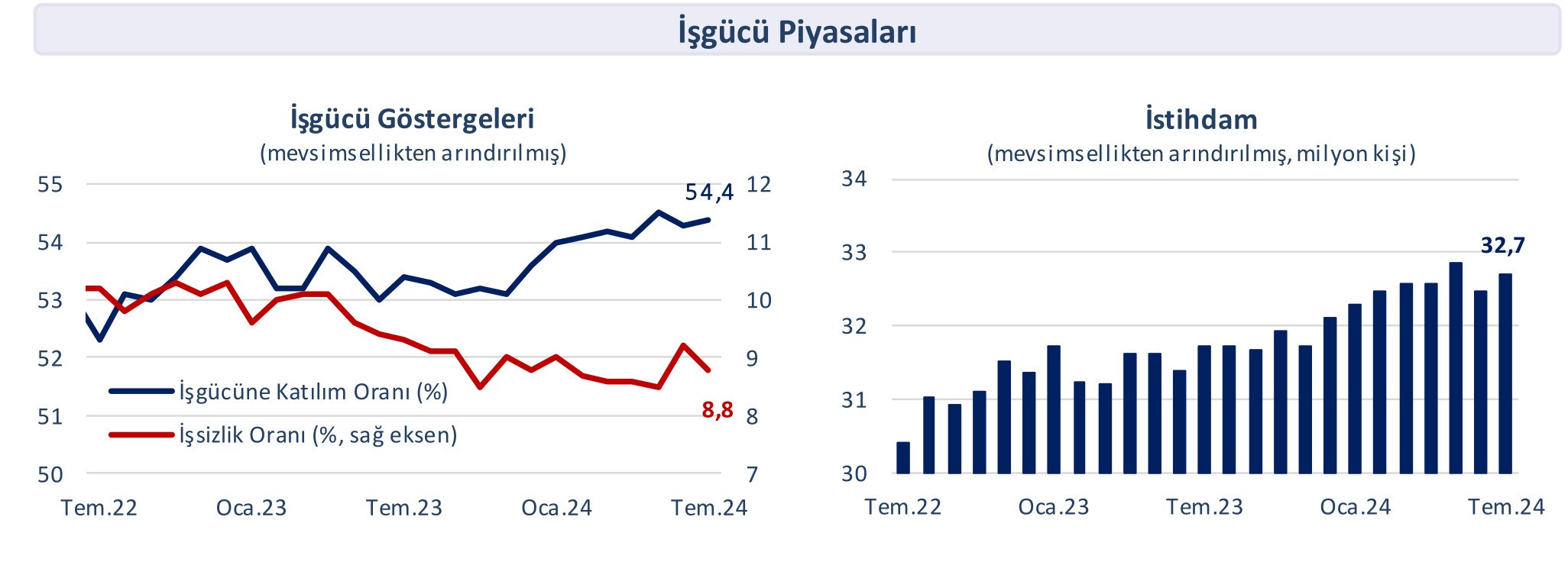
The seasonally adjusted unemployment rate decreased by 0.4 percentage points month-on-month to 8.8 percent in July, while the idle workforce rate also fell to 26.5 percent. According to calendar-adjusted data, the industrial production index contracted by 3.9 percent year-on-year in July.
ISO Turkey Manufacturing PMI fell to 44.3 in September, indicating a worsening of difficult operating conditions in the sector. The current account balance showed a surplus of 566 million USD in July, while the 12-month cumulative current account deficit decreased to 19.1 billion USD.
The central government budget deficit was 129.6 billion TL in August and 973.6 billion TL in the January-August period. In September, CPI increased by 2.97 percent month-on-month, exceeding market expectations, while annual CPI inflation decreased to 49.38 percent. In the same period, domestic PPI recorded an increase of 1.37 percent month-on-month and 33.09 percent year-on-year.
The CBRT, in its meeting on September 19, kept the policy interest rate unchanged at 50 percent, in line with expectations. The BIST-100 index decreased by 1.7 percent in September, while USD/TL recorded a limited increase of 0.3 percent on a monthly basis.
Medium Term Program published
In September, the Medium Term Program covering the 2025-2027 period was announced. In the program, where ensuring price stability was determined as the primary objective, GDP growth forecasts for 2024-2026 were revised downwards by 0.5 percentage points compared to the previous year's MTP forecasts, and were announced as 3.5 percent, 4.0 percent, and 4.5 percent, respectively. For the same period, year-end CPI inflation forecasts were revised upwards to remain within the forecast range announced in the CBRT's latest Inflation Report, and were stated as 41.5 percent, 17.5 percent, 9.7 percent, and 7.0 percent, respectively. The program forecasts the budget deficit's ratio to GDP to be 4.9 percent, 3.1 percent, 2.8 percent, and 2.5 percent, respectively, during this period.
According to the Sectoral Inflation Expectations report published by the CBRT, annual inflation expectations for 12 months later decreased by 1.2 percentage points to 27.5 percent among market participants, by 2.7 percentage points to 51.1 percent in the real sector, and by 1.5 percentage points to 71.6 percent among households. Thus, although household inflation expectations are still at high levels, they decreased again in September after a two-month increase. On the other hand, the proportion of households expecting inflation to fall in the next 12-month period decreased by 0.6 percentage points compared to the previous month, realizing at 29.0 percent.
CBRT did not change policy interest rate
In its meeting on September 19, the CBRT kept the policy interest rate unchanged at 50 percent, in line with expectations. In the decision text published after the meeting, it was stated that the main trend of monthly inflation did not show a significant change in August, and an improvement in services inflation was expected in the last quarter. The assessment that inflation expectations and pricing behaviors continue to pose a risk for the disinflation process was perceived as the CBRT maintaining its cautious stance.
However, the change in the statement from “the monetary policy stance will be tightened” to ”monetary policy tools will be used effectively” in the event of a significant and permanent deterioration in inflation supported expectations that the CBRT may review its current stance in the coming period. The CBRT made some changes in the reserve requirement application on September 21 to support the monetary transmission mechanism. Accordingly, reserve requirement ratios were increased from 12 percent to 15 percent for short-term TL deposits and from 8 percent to 10 percent for long-term TL deposits, while the TL facility ratio for FX deposits was reduced from 8 percent to 5 percent.
The equity portfolio of non-residents, adjusted for price and exchange rate movements, decreased by a net 69 million USD as of September 27 compared to the end of August, while the government debt securities (GDS) portfolio recorded an increase of 2.9 billion USD. Thus, since the end of 2023, there has been a foreign capital outflow of 2.0 billion USD from the equity market, while a foreign capital inflow of 17.4 billion USD occurred in the bond market. As of September 27, the CBRT's gross reserves were recorded at 157.4 billion USD, and net reserves at 54.1 billion USD.
Fitch upgraded Turkey's credit rating to “BB-”
International credit rating agency Fitch, in its assessment on September 6, following March, raised Turkey's credit rating by one notch to “BB-”, while changing its credit rating outlook from “positive” to “stable”. The agency stated that Turkey's international reserve composition strengthened due to decreasing dollarization and capital inflows, and emphasized that a possible early interest rate cut and a reversal from tight monetary policy would increase inflationary pressures, which could negatively impact the credit rating.

Unemployment fell to 8.8 percent
According to seasonally adjusted data, the unemployment rate decreased by 0.4 percentage points to 8.8 percent in July, following its rapid rise in June. This development was influenced by a decrease of 112 thousand in the number of unemployed individuals, despite an increase of 123 thousand in the labor force during the relevant period. Thus, labor force participation and employment rates rose to 54.4 percent and 49.6 percent, respectively, in July. During this period, the idle workforce rate, considered the broadest definition of the unemployment rate, also decreased by 2.7 percentage points compared to the previous month, reaching 26.5 percent.
Industrial production decreased by 3.9 percent year-on-year
In July, the calendar-adjusted industrial production index contracted by 3.9 percent year-on-year. While manufacturing production decreased by 5.1 percent, increases of 3.3 percent in the mining and quarrying sector and 8.2 percent in the electricity, gas, steam, and air conditioning sector limited the decline in the main index. Production losses were experienced year-on-year in 16 of the 24 sectors operating under manufacturing, with the sharpest decline of 23.3 percent observed in the manufacture of basic pharmaceutical products. In the same period, industrial production showed a moderate increase of 0.4 percent month-on-month, according to seasonally and calendar-adjusted data. It is considered that the low base created by bridge days between public holidays and weekends in June was effective in this limited increase. In July, the services production index also decreased by 0.2 percent month-on-month and 0.1 percent year-on-year, respectively.
Weakness in manufacturing sector deepened according to PMI data
Turkey's manufacturing PMI data published by the Istanbul Chamber of Industry (ISO) fell to 44.3 in September, indicating the sharpest slowdown in sector activities since May 2020. Challenging demand conditions led to the sharpest decline in new orders in approximately the last four and a half years, while the slowdown in export orders compared to the previous month also indicated a deterioration in external demand conditions. Production volume continued to decline for the sixth consecutive month, and consequently, employment recorded its most significant contraction since April 2020. Sectoral PMI data indicated that contraction was recorded in all 10 tracked sectors for the third consecutive month.
Confidence indices recorded an increase
According to seasonally adjusted data, the consumer confidence index increased by 2.4 percent compared to the previous month in September, reaching 78.2. When examining the sub-items of the index, it was noteworthy that assessments regarding the change in consumer prices over the past 12 months showed the fastest improvement with 24.6 percent. The seasonally adjusted real sector confidence index also rose by 1.2 percentage points month-on-month to 99.2 in September, after four consecutive months of decline. In September, the sectoral confidence index recorded a limited decrease of 0.2 percent month-on-month in the construction sector, while it increased by 2.5 percent in retail trade and 0.6 percent in the services sector, respectively. Thus, the economic confidence index increased by 1.9 percentage points in September, realizing at 95. In this period, the seasonally adjusted manufacturing industry capacity utilization rate increased for the first time after five months, albeit by a limited 0.2 percentage points month-on-month, reaching 75.9 percent.
Foreign trade deficit narrowed by 41.8 percent year-on-year
According to data published by TURKSTAT, exports increased by 13.8 percent year-on-year to 22.5 billion USD in July, while imports contracted by 7.8 percent, recorded at 29.8 billion USD. Thus, compared to July 2023, the foreign trade deficit decreased by 41.8 percent to 7.3 billion USD. The export coverage ratio also increased from 61.2 percent to 75.5 percent.
Current account balance posted a surplus of 566 million dollars
The current account balance recorded a surplus in July, following June. During this period, the current account surplus was 566 million USD, in line with market expectations, while the 12-month cumulative current account deficit decreased to 19.1 billion USD, reaching its lowest level since April 2022. In July, the year-on-year decrease in the balance of payments-defined foreign trade deficit (-52.7 percent) and the positive outlook in passenger transportation and travel revenues due to the tourism season were the main items supporting the current balance. In the first seven months of the year, the current account deficit, recorded at 16 billion USD, showed a 61.8 percent decrease compared to the same period of the previous year.
Capital inflow continued in direct investments
The capital inflow in net direct investments, which has continued since April, increased by 39 percent year-on-year to 670 million USD in July. During this period, direct investments by non-residents into the country were recorded at 1.2 billion USD, and direct investments by residents abroad were 510 million USD. Real estate investments directed domestically reached their highest value since April in July, at 289 million USD. On the other hand, according to newly released data by the CBRT, real estate investments made by domestic residents abroad amounted to 1.2 billion USD in the first seven months of the year.
Foreign trade data show that the year-on-year decline in the foreign trade deficit recorded in July continued with some acceleration in August. Despite difficulties in our main markets, the relatively positive assessments of external demand conditions by the ISO export climate index in August, as well as the increasing trend of travel revenues due to the tourism season, indicate that the current account deficit continued to decline during this period.
Central government budget posted a deficit
In August, central government budget revenues realized with a limited year-on-year increase of 12.5 percent to 690.7 billion TL, while budget expenditures rose by 45.8 percent to 820.3 billion TL. Thus, the central government budget posted a deficit of 129.6 billion TL in August. During this period, the non-interest budget deficit was 32.5 billion TL. In the January-August period, the central government budget deficit increased by 153.9 percent compared to the same period last year, reaching 973.5 billion TL.
In August, despite a relatively moderate increase in expenditures compared to annual CPI inflation, a very limited rise in tax revenues led to the continued expansion of the central government budget deficit. On the other hand, the cumulative budget deficit, which rose to 973.6 billion TL in the January-August period, constituted 45.3 percent of the 2,149 billion TL target set for the full year in the Medium-Term Program covering the 2025-2027 period, indicating that the actualizations continued to be in line with the plan.
CPI increased by 2.97 percent month-on-month
In September, CPI recorded an increase of 2.97 percent month-on-month, exceeding market expectations. According to CBRT Market Participants and Reuters surveys, the expectation was a 2.2 percent monthly increase in consumer prices. However, due to the high base effect, annual CPI inflation continued its downward trend for the fourth month, falling to 49.38 percent, its lowest level since July 2023. In September, domestic PPI increased by 1.37 percent month-on-month, while annual domestic PPI inflation realized at 33.09 percent, its lowest level since March 2021.
In September, the group that contributed the most to the monthly domestic PPI increase was food products, with 0.33 percentage points. Additionally, the electricity, gas production and distribution group continued to make a high contribution to monthly inflation with 0.21 percentage points during this period. The groups that recorded the fastest price increases in September were tobacco products (8.30 percent), coal and lignite (4.90 percent), and metal ores (3.76 percent), respectively. During this period, the group that saw the largest monthly price decrease was coke and refined petroleum products (5.51 percent).
Although annual CPI inflation continued its downward trend in September, falling below 50 percent for the first time since July 2023, the monthly CPI increase and core indicators pointed out that the improvement in the main trend of inflation has not yet been fully achieved. In this context, September data increased the importance of inflation's course in October and November. In the coming period, the extent to which the CBRT's anticipated improvement in high services inflation will materialize in the last quarter of the year, and the impact of recently increasing geopolitical risks on oil prices will be closely monitored.
Fed's interest rate decision supported global risk appetite
Global risk appetite, which was under pressure in the first half of September due to investors' cautious approach before the Fed's decision, followed a positive trend after the Fed's rapid interest rate cut. Thus, in September, MSCI world and emerging market indices recorded increases of 1.7 percent and 6.4 percent, respectively. While the S&P 500 and Dow Jones indices completed September at historical high levels, the US 10-year Treasury bond yield and the DXY index decreased by 13 basis points and 0.90 percent month-on-month, respectively. The price of an ounce of gold, which tested its historical high of 2,670 USD during the month, completed September with an increase of 5.3 percent at 2,634.49 USD.
Domestic markets followed a volatile course in September, diverging negatively from global markets. The BIST 100 index decreased by 1.70 percent month-on-month to 9,665.78. In September, the yield on the 2-year benchmark bond fell to 42.1 percent, while the five-year CDS risk premium decreased by 9 basis points, ending the month at 266 basis points.
Source: İş Bankası
This content has been translated using artificial intelligence technology.

